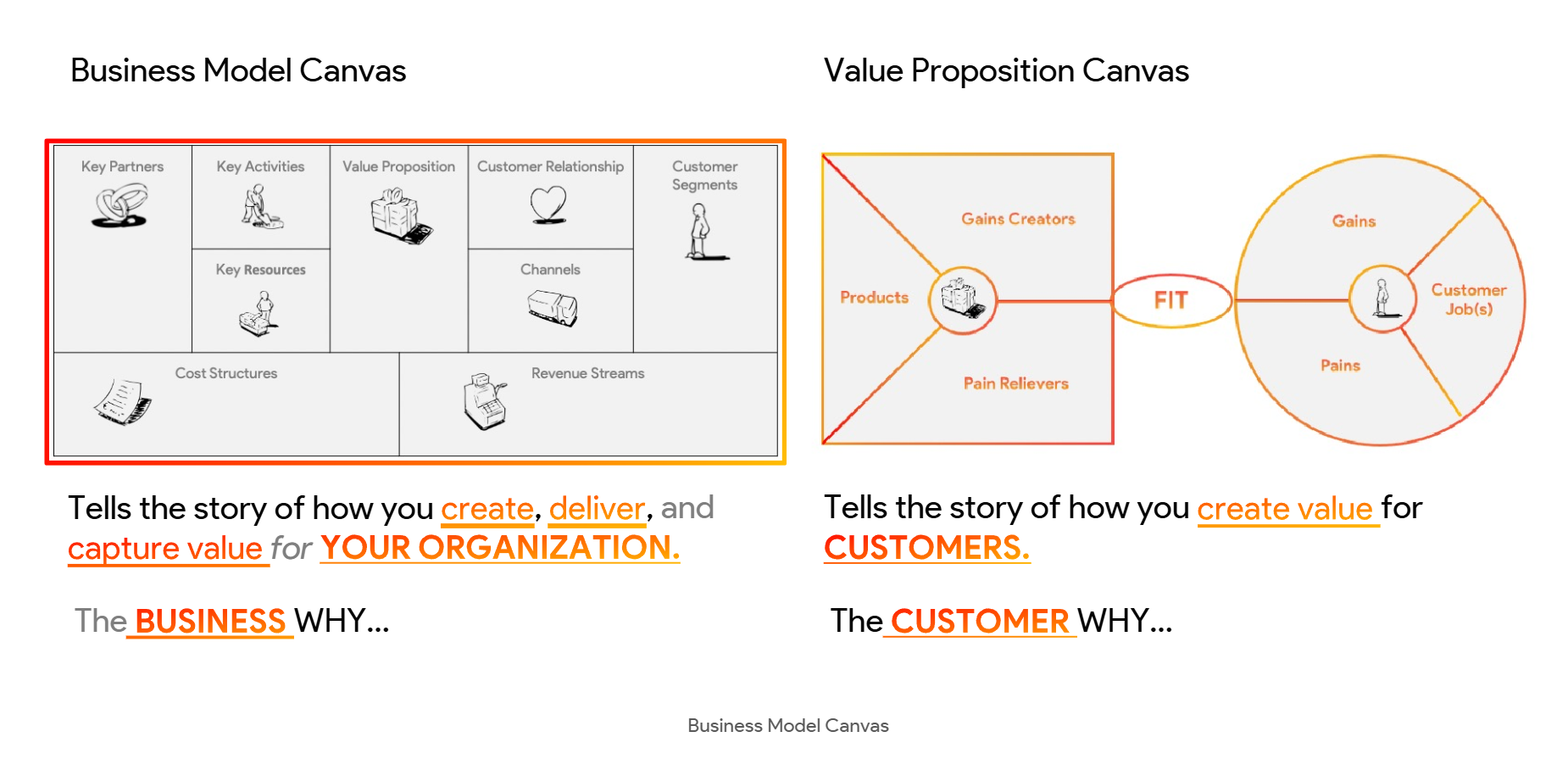
VALUE PROPOSITION CANVAS (VPC)
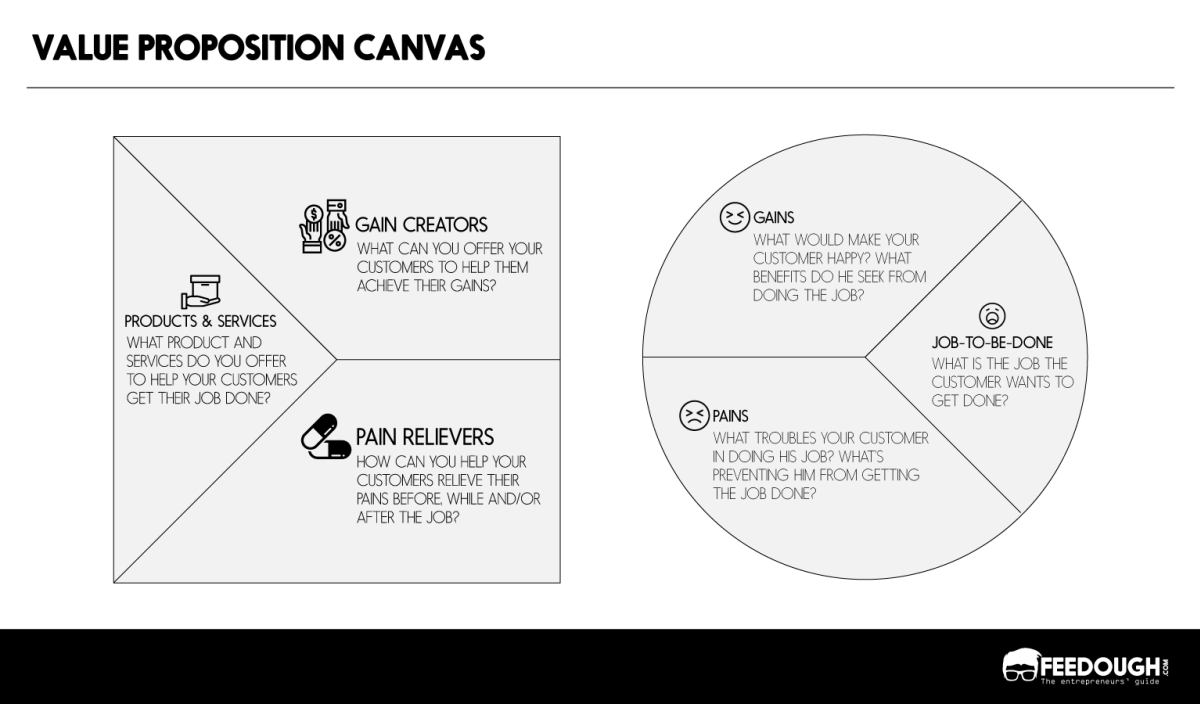
Customer Profile
Understand your target customer’s context, tasks, frustrations, and expectations.
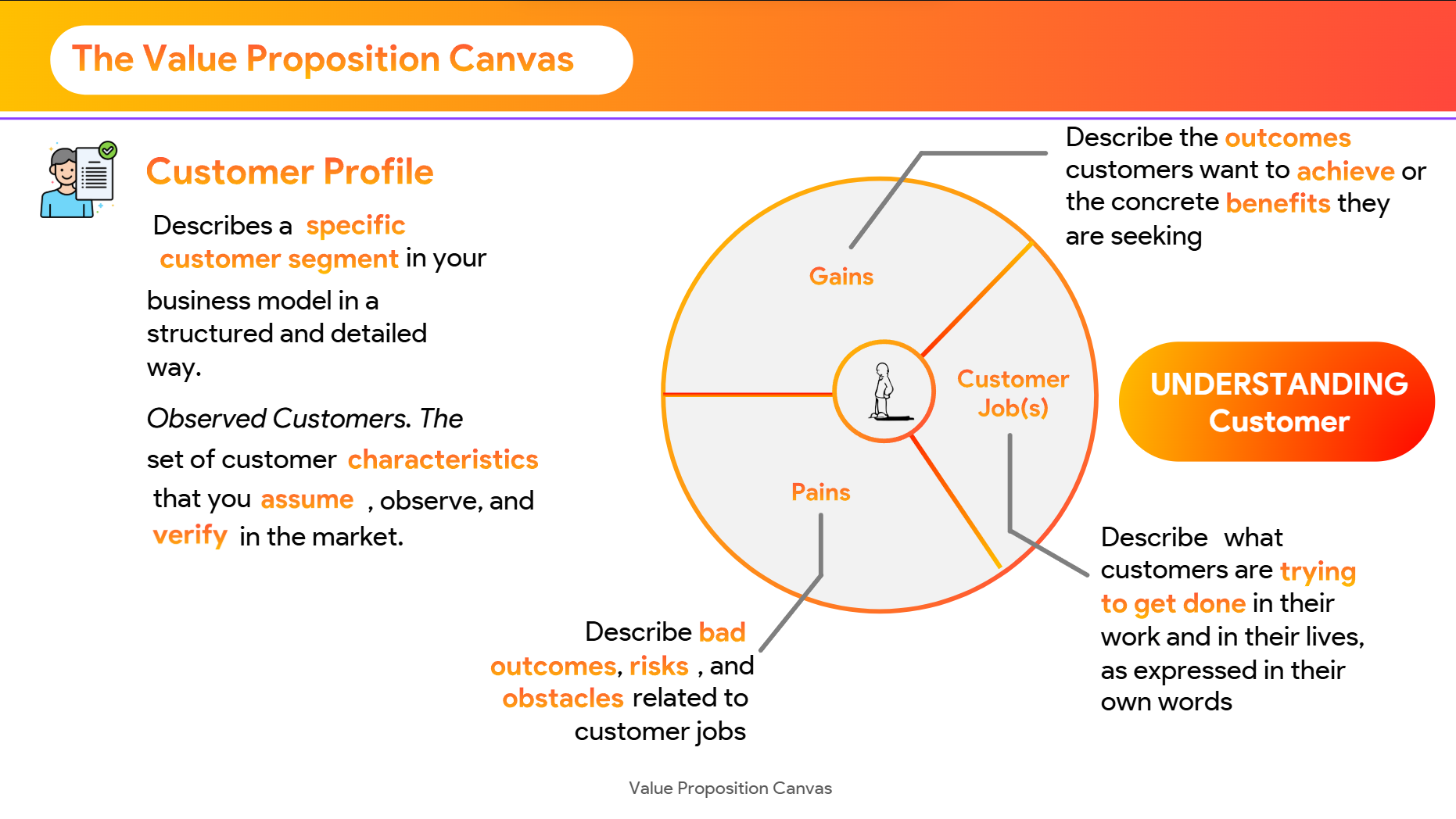
1. Customer Jobs
What the customer is trying to get done in their work or personal life.
- What tasks are your customers trying to complete?
- What problems are they trying to solve?
- What social, emotional, or functional jobs do they have?
- What goals or outcomes are they aiming to achieve?
Example: A school administrator wants to track teacher performance, automate class schedules, and gain insights for reporting and recognition.
2. Pains
The challenges, risks, or inefficiencies that prevent the customer from achieving their goals.
- What annoys or frustrates your customers during their tasks?
- What are the main obstacles or risks they face?
- What costs (time, money, effort) do they want to avoid?
- What negative outcomes do they fear?
Example: Manual data encoding takes hours. Mistakes in reports affect credibility. Lack of digital tools increases stress.
3. Gains
The positive results or outcomes your customer hopes for, including unexpected benefits.
- What benefits or outcomes do your customers desire?
- What would make them happy or satisfied?
- What features or improvements would exceed expectations?
- What savings or performance boosts are they looking for?
Example: Automating reports, reducing admin work, and accessing predictive insights to make better decisions.
Value Map
Describes how your product or service addresses each of the customer’s jobs, pains, and gains.
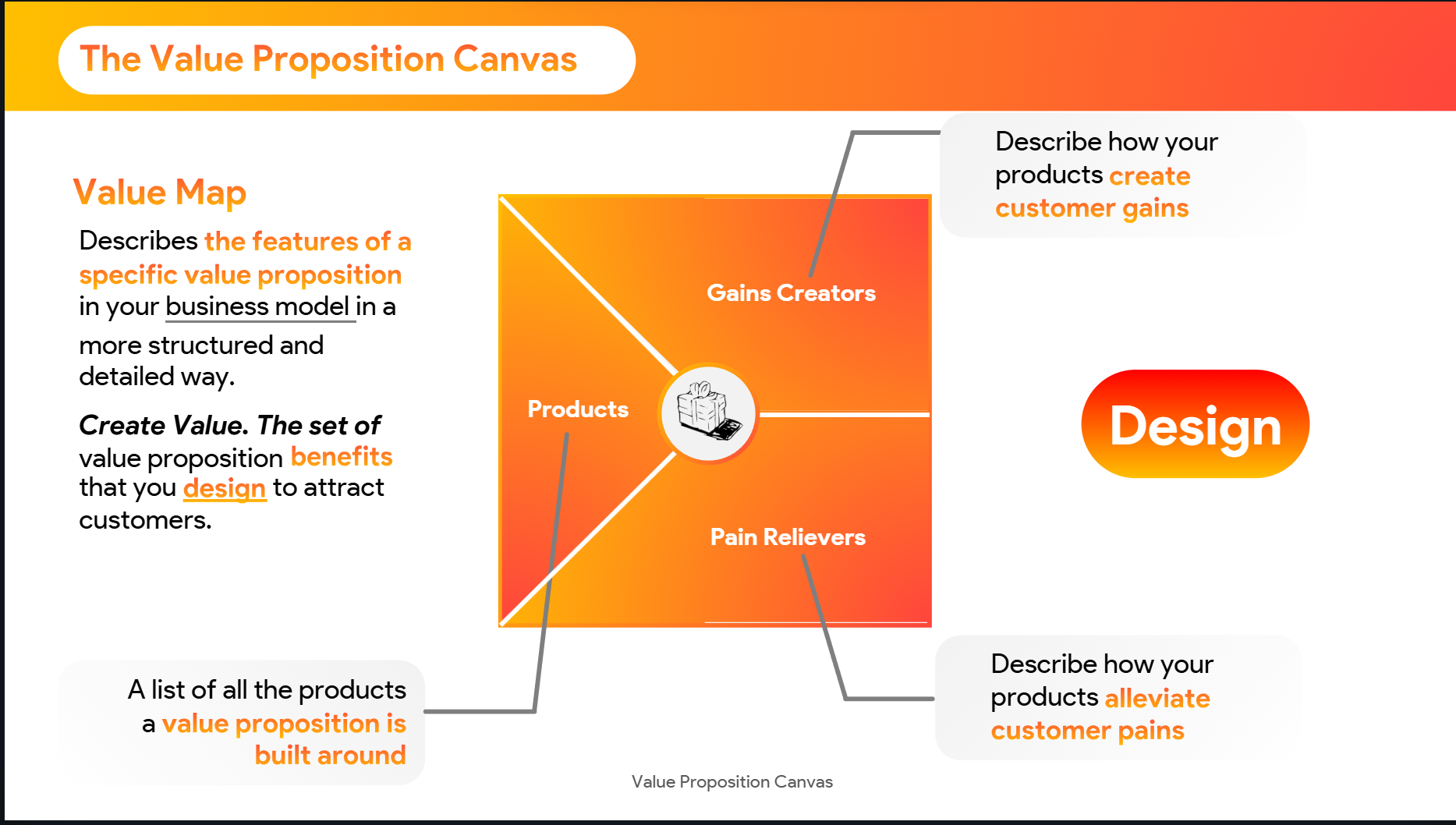
1. Products & Services
Everything you offer that helps your customer perform jobs and reach goals.
- What are you offering to your customers?
- What tools, features, or services do you provide?
- What formats or delivery methods do you use?
Example: Web platform with analytics dashboard, chatbot assistant, and downloadable reports.
2. Pain Relievers
How your product eliminates or reduces pain points.
- How does your solution eliminate or reduce frustrations?
- How do you address common complaints or inefficiencies?
- How do you help customers avoid risks or losses?
Example: Auto-scheduling, error-free report templates, real-time data syncing.
3. Gain Creators
How your product enables or enhances the customer’s desired outcomes.
- How does your solution create additional value or benefits?
- How do you make customers’ lives easier or better?
- How do you help them achieve or exceed their goals?
Example: Predictive analytics to plan better, alerts for anomalies, custom reports for stakeholders.
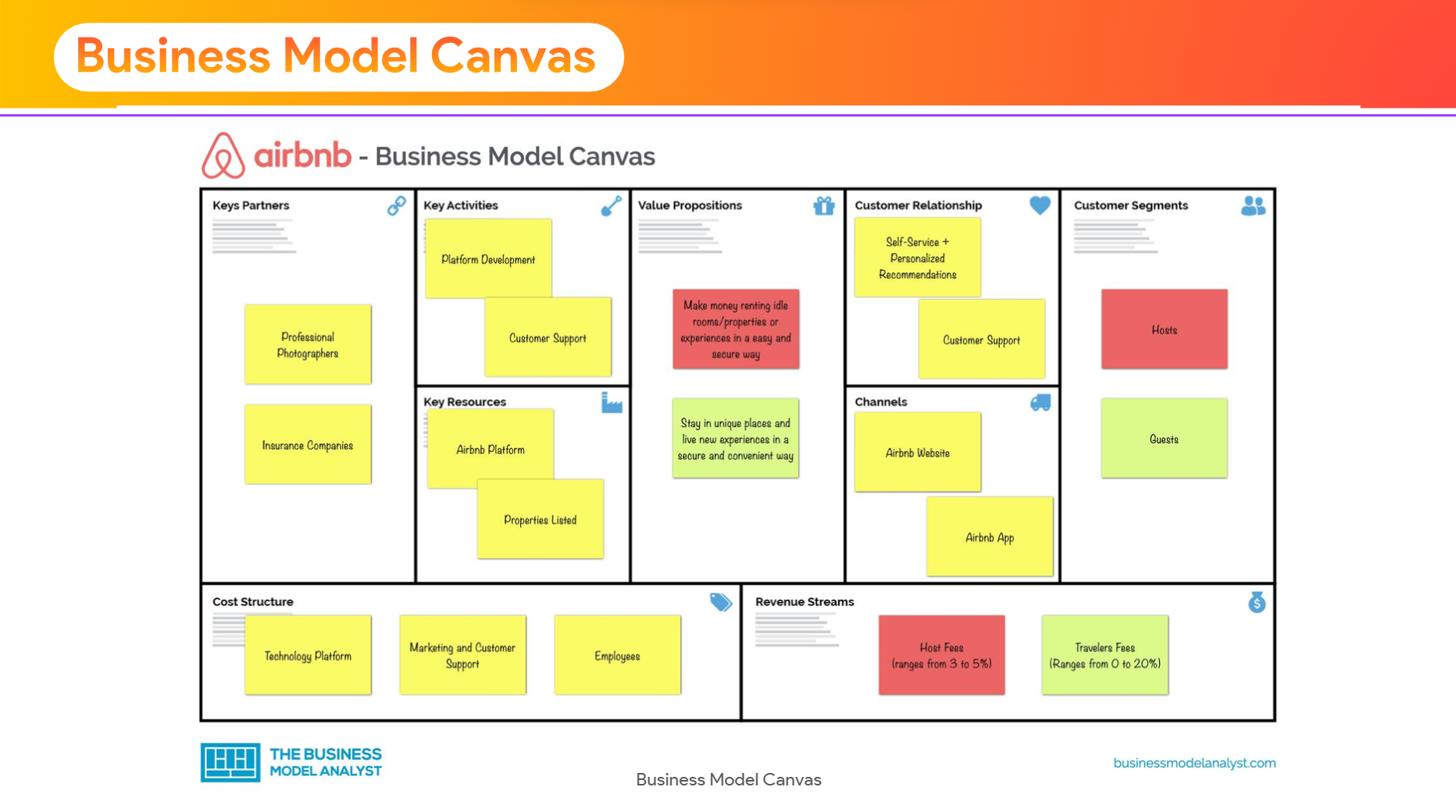
BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS (BMC)
A strategic blueprint showing how your business delivers and captures value.
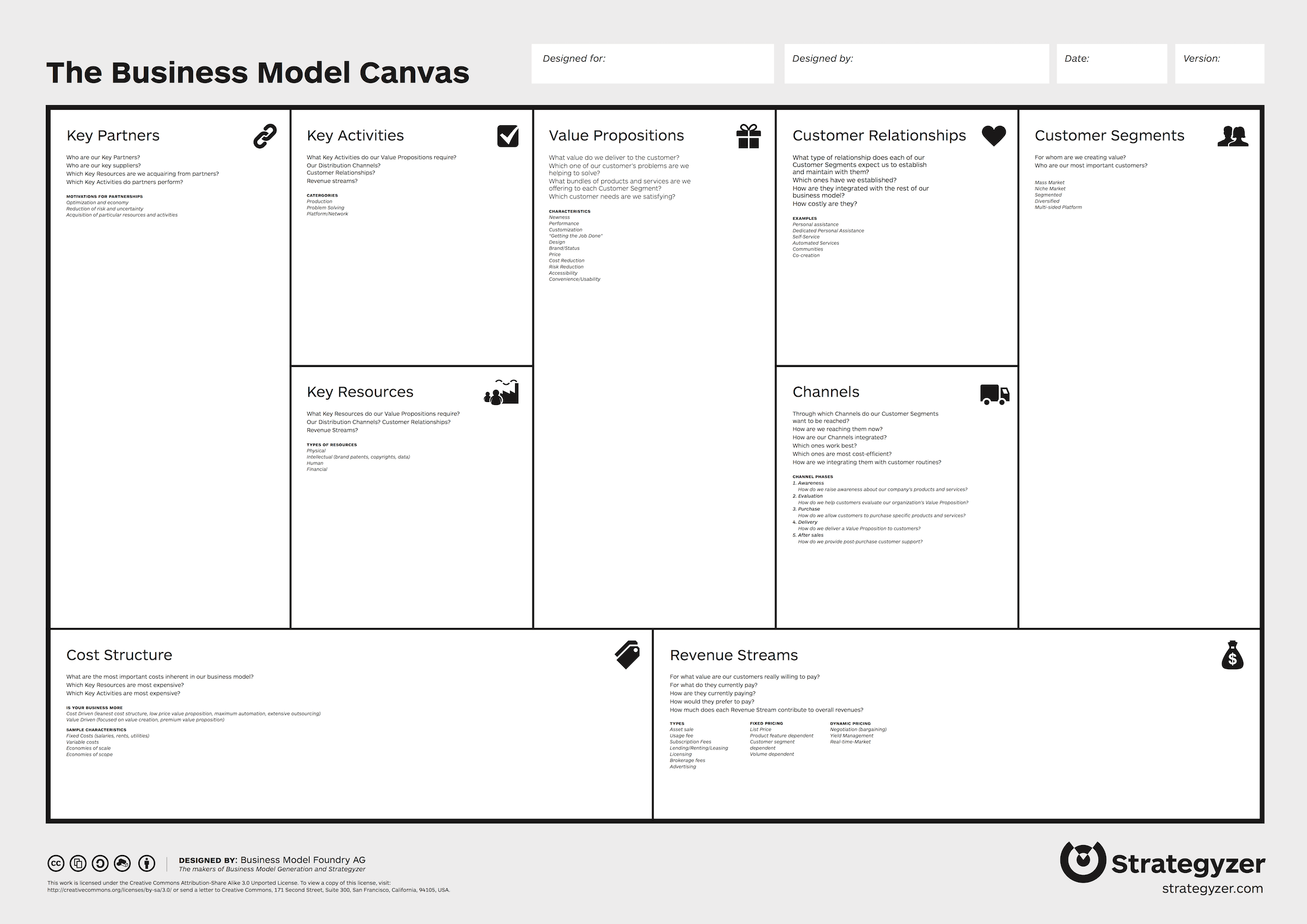
1. Customer Segments
The specific groups your business serves.
- Who are your target users or buyers?
- What are their key characteristics or needs?
- Which groups are underserved or most valuable to reach?
Example: Teachers in rural schools, small business owners, freelance consultants.
2. Value Propositions
The value you offer to each customer segment.
- What problems are you solving for each segment?
- What makes your solution unique or better?
- What benefits do you promise to deliver?
Example: “Save time and reduce stress by automating daily admin tasks.”
3. Channels
How you reach and deliver value to customers.
- How do you communicate with your customers?
- Through what means do you deliver your product or service?
- Which channels do customers prefer?
Example: Online platform, mobile app, YouTube tutorials, onboarding webinars.
4. Customer Relationships
How you interact with customers across the journey.
- How do you build and maintain customer loyalty?
- What type of relationship do customers expect?
- How personalized or automated is the interaction?
Example: AI-assisted onboarding, live chat support, and a knowledge base.
5. Revenue Streams
How your business earns income.
- How do you earn income from your value propositions?
- What are customers willing to pay for?
- What pricing model(s) do you use?
Example: Monthly subscription, pay-per-use, enterprise licensing.
6. Key Resources
The critical assets needed to create value.
- What assets are essential to deliver your value?
- What human, financial, or intellectual resources do you need?
- What tools, platforms, or facilities are required?
Example: AI developers, customer success team, secure cloud servers.
7. Key Activities
The core actions your business must perform to succeed.
- What core operations must be performed well?
- What processes are needed to deliver your solution?
- What activities support growth and sustainability?
Example: Feature updates, user training, bug fixing, community engagement.
8. Key Partnerships
The external collaborators that help you succeed.
- Who helps you deliver your value proposition?
- Which partners or suppliers are strategic to your success?
- What roles do they play in operations or distribution?
Example: Google Cloud for infrastructure, government edtech grants, pilot schools.
9. Cost Structure
The major expenses of running the business.
- What are your biggest cost drivers?
- Which resources and activities are most expensive?
- How do your costs align with your revenue model?
Example: Developer salaries, hosting, data storage, marketing and sales.